Tendons are tough, cordlike structures that connect muscles to bones. They are responsible for transmitting muscle force to bone and as such are needed for allowing body movement and overall joint stability.
"Tendons are rich in collagens with the most abundant tendon component being type I collagen, constituting about 60% of the tendon and about 95% of the total collagen. The remaining 5% consist of type III and V collagens. In normal tendons, type III collagen is mainly located in the endotenon and epitenon. However, it is also found in aging tendons and at the insertion sites of highly stressed tendons such as the supraspinatus. Type III collagen forms smaller less well organised fibrils and type I collagen, which may result in decreased mechanical strength."
"Tendon Healing Mechanobiology | Shoulderdoc By Prof. Lennard Funk". 2019. Shoulderdoc.Co.Uk. Accessed May 16 2019. https://www.shoulderdoc.co.uk/article/1029.
Despite the fact that they are ropelike, tendons are actually living tissue; they can and do change properties over time depending on external factors - most physical. With appropriate physical training, tendons will respond by increasing in size and strength. However, if physical training is not done appropriately it leads to overuse injuries which means the tendon will typically undergo inflammation. It is further known by the medical community that lack of use of tendons (immobilisation) will lead to a reduction in stiffness, strength and total weight of the tendon. There have been studies done showing that immobilisation of a tendon will cause uneven and irregular collagen fibres, resulting in a tendon less able to handle high stress loads before breaking down.
Tendonitis / tendinitis (pronounced "tendonitus") means you are suffering from a condition where a tendon in your body is injured, inflamed or irritated. There are many tendons in our bodies that are made of fibrous cords of tissue that attach muscles to bones.
Anyone can suffer from tendonitis, but it's most common in adults due to degeneration of tissue as we age. If you have tendonitis you'll usually feel pain located where your injury is and in the surrounding area. If you suffer from a tendon rupture (ruptured tendon) you might hear a sudden pop or experience severe pain immediately after you're injured. Tendon ruptures usually only happen from accidents or pre-disposed conditions that weaken the tendon - like repeated anti-inflammatory injections, calcium deposits (spurs) around a joint or other diseases (ie. gout). Tendon ruptures usually require surgery to re-attach the tendon to the bone, and if left untreated can result in permanent disability of the affected area.
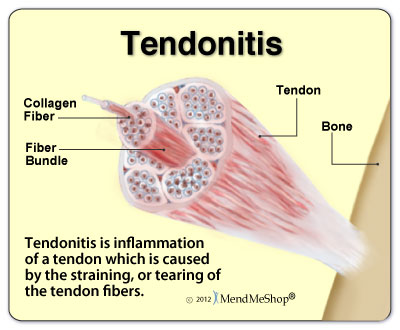
Immediate tendon injury treatment usually consists of avoiding any activity that makes your pain worse (or caused your injury in the first place), resting your injured area, icing the area, and taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) (reference: 1).
You might be suffering from a Tendon Injury such as Tendonitis if:

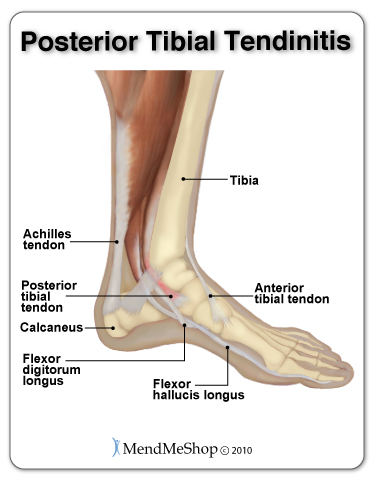
If you're suffering from some of those symptoms and now wondering why your injury is taking so long to heal, it's important for you to know that tendonitis is an inflammatory condition where the pain, swelling and inflammation can go on for weeks or even months.
You could have acute tendonitis (an injury that happened suddenly from an accident or from overuse / repetitive actions) or chronic tendonitis (an injury or re-injury that weeks, months or even years old). Either way your tendonitis injury will have a painful impact on the quality of your life.
At this point your mobility - like your ability to walk, run, jump, carry or pick up object or other activities that you would normally do - is probably impaired... Leaving you with very limited range of motion in the affected area or joint.
Healing your tendonitis can be a difficult task, especially if you're suffering from pain in a general area and have no idea what type of injury you're facing.

Everyone will strain their tendon at least once in their lifetime. Straining your tendon is a common injury but the trick with a strained tendon is to make sure it heals properly which will provide the lowest chance of re-injury.
Re-injury of a strained or stressed tendon happens more easily than the original injury. When your tendon is re-injured there's also usually more inflammation. Tendonitis is a degenerative condition in the tendon fibers that attach muscles to bone. People with tendonitis generally complain of a severe, burning pain in the area, that gradually gets worse and becomes even more painful from stress on the joint.
If you have tendonitis that's from working out or exercising, you should heavily reduce your workout intensity through the healing stage and make sure the injured tendon is warmed up (and cooled down) properly before and after a workouts. When treating tendinitis, rest the area, apply cold compression for 10-20 minutes at a time for at least 3 times a day. Do this to the injured area for the first day up to 3 days.
There are many kinds of tendonitis affecting different areas of the body. Some forms of tendonitis include:
A group of tendons on the top, bottom and along the sides of the foot connect muscles in the leg to the bones in the arch and toes of the foot. A strain to one of the tendons will cause pain in your arch and toes and make it difficult to walk. Posterior Tibial Tendonitis is the most common form of foot tendonitis. These injuries can be caused from over-use, improper stretching or poor form while walking or during any physical activity. Some people with arch issues (ie. that have a flat foot) or arthritis will be at risk of getting tendonitis.
Sesamoiditis is another form of foot tendonitis that's not often thought about. You will know if you have sesamoiditis if you experience most of your pain in the ball of your foot.
Click here to learn more about:
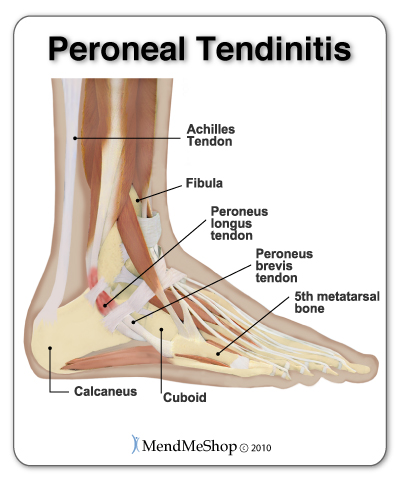
With this injury you'll feel pain in your ankle, swelling and your ankle may feel warm to the touch. You might also feel some weakness or instability in your foot and ankle joints. Severe ankle tendonitis (tendinosis) may increase the height of the arch in your foot. The most common form of ankle tendonitis is Peroneal Tendonitis. If left untreated, ankle tendonitis could turn into tendinosis or a complete tendon rupture.
Click here to learn more about:
One of the major tendons in the leg to get injured is the plantaris tendon. This tendon is in the middle of the calf muscle, on the back of the leg and attached to the Achilles tendon (a major tendon just above the back of your heel). A tear of the plantaris tendon can cause pain in the calf muscle (sometimes described as a stabbing pain) and if the tendon is ruptured there might be a sudden pop. This injury usually occurs during sports or related activities like Tennis. Plantaris tendonitis is also referred to as "tennis leg" or related to tennis leg (calf muscle) injuries.
Tendons in the knee usually get injured from athletic or sporting activities like rugby, football, volleyball, or any activity involving running and jumping. Individuals with arthritis or osteoarthritis in their knee may also experience knee tendonitis due to the degeneration of bone and tissue in their knee joint. The most common type of knee tendonitis is patellar tendonitis, also sometimes referred to as 'jumper's knee'. If you have knee tendonitis some of the symptoms you'll experience are pain, swelling and inflammation around the injured area. The severity of your pain depends on the amount of damage that's been done to your tendon. Some other common forms of knee tendonitis include quadriceps tendonitis, pes anserine tendonitis, hamstring tendonitis and popliteus tendonitis.
Click here to learn more about:
This kind of injury usually happens from overuse of the tendons in the hip and thigh from activities like running, cycling, football, hockey or soccer. If you've suddenly increased your activity level to include exercise, cardio or any other sporting activity then you might be at risk of getting hip or thigh tendonitis. If you suffer from gluteus medius tendonitis you'll probably notice more pain when walking and a weakness in your legs. This type of tendonitis may also be caused by a difference in the length of your legs (leg-length discrepancy).
Other forms of tendonitis - like iliotibial band syndrome (ITBS) or adductor tendonitis - can present pain in different areas. IT Band syndrome may cause pain on the side of your hip that radiate down to your knee (the IT Band is connected to your hip AND knee). Hip alignment issues or regularly running may cause this condition. Adductor tendonitis may transfer pain into your inner thigh. This condition is also usually experienced by individuals who play hockey, football or soccer. For this injury, pain will be felt when stretching or twisting your torso during exercise or athletic activity.
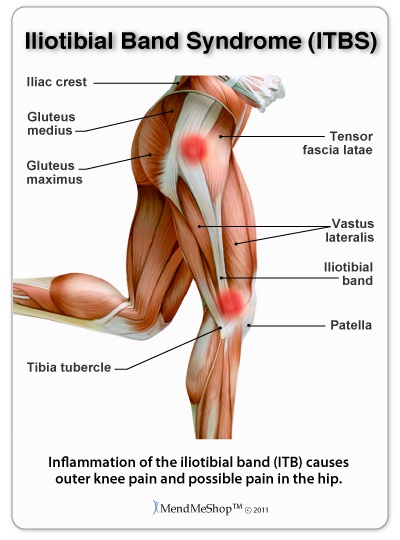
Click here to learn more about:
Tendonitis of the wrist (extensor / flexor tendonitis) usually happens from overuse of the hands and wrists. This can happen from certain jobs that require a lot of hand / wrist movement (ie. assembly line work, tailor, production sewer, mechanic, gardener, painter, office worker, cashier, etc). Although it hasn't been medically proven, tendonitis in the wrist and hand can sometimes be linked to extended use of computer keyboards and other handheld devices (mobile phones, PDAs, gaming systems). With this injury you'll feel pain and swelling in your wrist or hand, and extreme cases may have some nerve damage (carpal tunnel syndrome) with atrophy (wasting away) of the thumb muscle. Other conditions like de Quervain's tendonitis, and thumb tendonitis may mean a thickening of the tissue in your thumb or your pointer finger may be permanently stuck in a bent position (sometimes referred to as 'trigger finger' or 'trigger thumb').
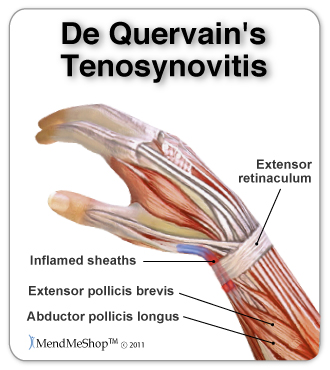
Click here to learn more about:
The triceps tendon is the major tendon of the arm and this tendon connects the triceps muscle to the bony point of the elbow. Full rupture of the tricep tendon in the arm is one of the rarest tendon injuries and can usually only happen after some kind of trauma (accident). If you have tricep tendonitis you'll experience pain, swelling and inflammation around the top of your elbow.
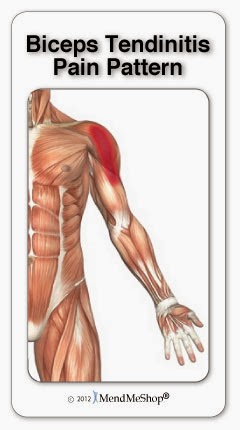
The biceps tendon is in the upper arm attaching at the front of the shoulder. This is more commonly injured than the triceps tendon and is more apt to occur. The distal biceps tendon is on the other end of the biceps muscle and attaches to the forearm just ahead of the inner elbow location. Injuries to both of these tendons is relatively common, especially for those that often handle heavy items. Most at risk are bodybuilders, certain types of athletes that depend on arm strength and heavy manual laborers.
Forearm tendonitis injuries are common injuries and are easily treated with the leg/arm TShellz Wrap®. In such cases pain, swelling and inflammation will be felt in the forearm, usually when holding heavy objects or even just from typing on a keyboard (overuse injury). In all cases, the Arm / Leg Cold Compress or Ice Pack will reduce pain, swelling and inflammation while treatment with the Arm/Leg TShellz Wrap® will help mend the damage and increase Blood Flow to the injury, resulting in a faster healing time.
The best part about the Leg/Arm wraps are their universality. They can be used pretty much anywhere on the arms or leg - wherever there the pain may be.
Golfers Elbow is one of the most popular forms of acute tendonitis and is most prevalent in females. Elbow injuries account for 35% to 33% of all injuries in amateur golfers. Golfers Elbow is a very painful condition affecting the inside of the elbow (close to the "funny bone") and results from overuse of arm and forearm muscles, or hitting an obstruction (ground, root, etc) instead of the golf ball during a hard swing.
Tennis elbow is a form of tendinosis which means chronic degeneration of the tendon or tendons. You will have tenderness on and around the tendons that attach to the small bony part on the outside of your elbow (lateral epicondyle), and perhaps a bit of swelling but not much. Tennis Elbow tendinosis is commonly caused from the overuse of the tendons located in your forearm that help to extend your wrist and fingers. The wear and tear on these tendons is a result of small tears in your tissue that don't heal properly. The inability of your tendon to heal properly causes the tendons to weaken until the tissues become very thin, and eventually wear out.
Click here to learn more about:
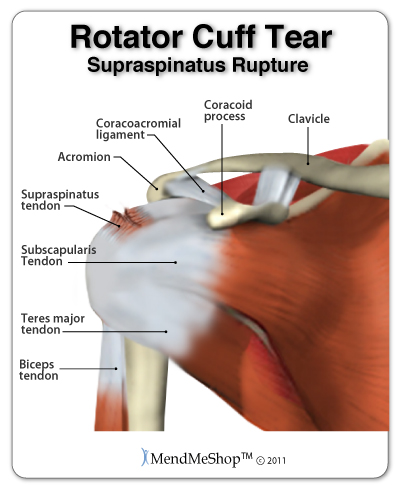
Your shoulders are the most mobile joints in your body. The most common forms of shoulder tendonitis include calcific tendonitis, supraspinatus tendonitis (rotator cuff tendonitis) and bicep tendonitis. Calcific tendonitis is a condition where bone (a calcium deposit) has grown in the middle of one of your rotator cuff tendons. The causes of this injury are still a mystery to many medical professionals, but the body can eventually (over time) re-absorb the calcium deposit so it will disappear.
Supraspinatus tendonitis can sometimes happen with shoulder impingement syndrome. Individuals that work in jobs with repeated overhead activity and athletes participating in swimming, tennis and volleyball are most affected by this injury. If you have supraspinatus tendonitis you'll experience pain, swelling and inflammation on the side of your shoulder (around the deltoid muscle).
Much like supraspinatus tendonitis, bicep tendonitis is caused by repetitive overhead activities like swimming, tennis and baseball or even lifting weights. If you have bicep tendonitis you'll experience pain, swelling and inflammation at the front of your shoulder. Bicep tendonitis is a common condition that occurs with other problems in the shoulder joint.
Click here to learn more about:
Product Advisors are available 9:00 am to 5:00 pm Eastern Standard Time Monday to Friday.
I want to learn more about Post-Surgery Recovery
I want to learn more about TShellz Wrap® Circulatory Boost
I want to learn more about Ice & Heat: Which Is Better For Treatment?
I want to learn more about Tendonitis Treatments
I want to learn more about Tendonitis Surgery
During your recovery, you will probably have to modify and/or eliminate any activities that cause pain or discomfort at the location of your soft tissue injury until the pain and inflammation settle. The more diligent you are with your treatment and rehabilitation, the faster you will see successful results!
Please be aware that this information is neither intended nor implied to be a substitute for professional medical advice. CALL YOUR HEALTHCARE PROVIDER IMMEDIATELY IF YOU THINK YOU MAY HAVE A MEDICAL EMERGENCY. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider before using any of our outstanding products to make sure they are right for you and your condition or if you have any questions regarding a medical condition. Always see your doctor for a proper diagnosis as there are often many injuries and conditions (some very serious) that could be the cause of your pain.
© 2025 In.Genu Design Group, Inc. Contact Us