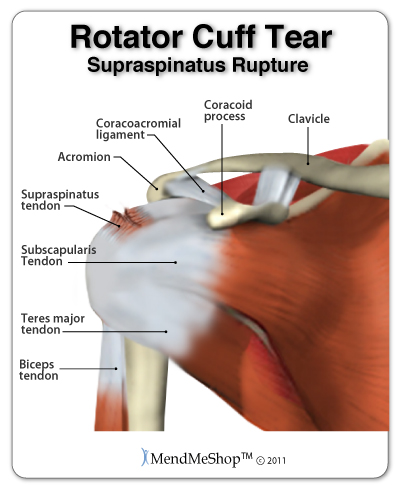
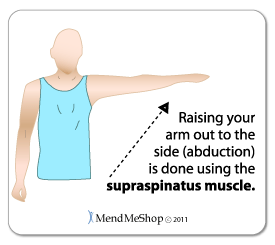
The supraspinatus tendon is often the tendon that is injured in a rotator cuff injury although not always. It usually starts with tendinitis - often fraying begins to occur as the tendon thickens and rubs against the acromion or a tear results from an extreme stress. Tears often occur gradually, though many are associated with sports injuries (especially baseball and swimming), falls on the shoulder, or an added injury due to shoulder dislocation in elderly folk. If you've ever been diagnosed with bursitis, it's possible the supraspinatus tendon is the true source of your pain, not the shoulder bursa. In this case, the pain does not resolve with typically prescribed anti-inflammatory medications.
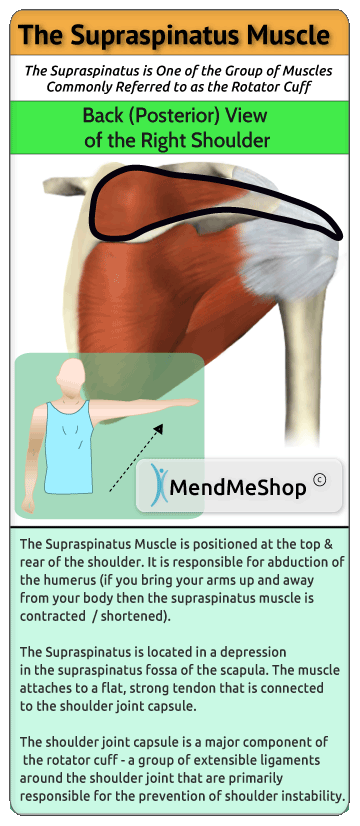
The rotator cuff is a term given to four main tendons that wrap around the shoulder joint, the supraspinatus tendon being the tendon coming off the shoulder blade in the top portion.
Rotator cuff tendonitis (also spelled tendinitis) and tears often occur gradually, though many are associated with sports injuries (especially baseball and swimming), falls on the shoulder, or an added injury due to shoulder dislocation in elderly folk. If you've ever been diagnosed with bursitis, it's possible the supraspinatus tendon is the true source of your pain, not the shoulder bursa. In this case, the pain does not resolve with typically prescribed anti-inflammatory medications.
The supraspinatus is the most commonly injured tendon in the rotator cuff. You might be suffering from a supraspinatus tear (or supraspinatus tendinitis) if:
If you are experiencing any of those symptoms then you might have a supraspinatus tear injury. The location, type of tear and any other injuries in the joint can greatly influence your ability to recover from and heal your torn supraspinatus tendon.
If you've suffered a traumatic sudden injury to your shoulder, you may have heard a sudden popping sound or felt a tearing sensation in your shoulder. Swelling around your shoulder will happen within a few hours after the injury or in the following days. If the injury is severe enough, you may also have some bruising on your shoulder. Immediate, intense, pain will follow - especially when you try to raise, lower, or rotate your arm.
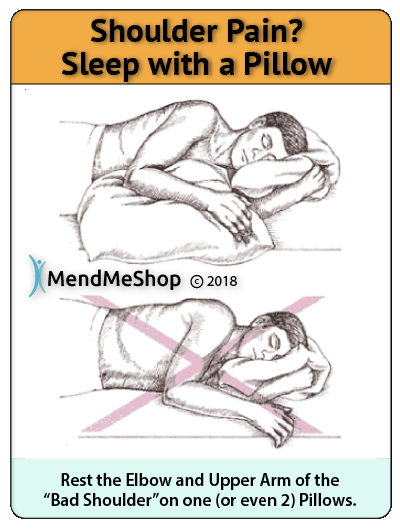
If your rotator cuff tear is big enough you might feel weakness (instability) in your shoulder. Over time this weakness will turn into a limited range of motion and inability to raise, lower, or rotate your arm - resulting in pain. At this point your rotator cuff injury would also be interfering with your sleep, causing pain and night and forcing you to wake up several times to adjust your sleeping position.
Degenerative rotator cuff tears are subtle with pain that increases over time. You may also notice swelling after exercise or daily activities. If you do have pain, you may experience something called 'trigger point pain' in your shoulder and possibly feel weakness / instability. Trigger point pain is pain that comes from a specific spot in your rotator cuff muscle that has become a hypersensitive area. These trigger points, or hypersensitive areas of pain, are known to be a source of on-going pain and lack of blood flow within the tissue. Pain may increase with certain activities, like raising your arm to reach for something off of a high shelf, brushing your hair or teeth, getting dressed, or reaching behind your back.

If you're suffering from a chronic rotator cuff injury you may have developed a sticking or freezing sensation in your arm. This freezing sensation (where mobility is completely reduced) may be a sign of another injury called frozen shoulder or adhesive capsulitis.
Other symptoms, like a crackling sensation (crepitus) in your shoulder, could be a sign of degenerative conditions in your arm. This may mean you are suffering from arthritis or osteoarthritis (especially is the crackling occurs with consistent snaps or pops).
Rotator cuff injuries are almost like a domino affect. As soon as one area of the tissue is damaged, other areas can get torn or strained as well. It's entirely possible to be suffering from a rotator cuff tendinitis tear injury, strained rotator cuff muscle and also develop a bone spur in your shoulder. A rotator cuff tear in the tendon or muscle could also lead to impingement syndrome (where your tendon or bursa gets caught between the bones in your shoulder). If left untreated, a rotator cuff tear injury can also lead to frozen shoulder (adhesive capsulitis) - a shoulder joint injury that causes thickening of the shoulder joint capsule that basically 'freezes' your arm and shoulder in place (with an inability to move, raise, or lower your arm).

Anyone can injure their rotator cuff badly, though rotator cuff tears happen most often from sudden or traumatic accidents and overuse or repetitive stress. A fall, lifting or pulling an object that's too heavy, accident, or injury during a sporting activity can all cause sudden trauma to the rotator cuff. Athletes that play sports where they repeatedly use their arms in raised and lowered positions - such as baseball players, swimmers, tennis players, and football players - are often affected by rotator cuff tears.
It's much more likely for someone who is young to get a torn rotator cuff through an accident or sudden traumatic event. In comparison, overuse and repetitive movement injuries can affect everyone due to degeneration of their rotator cuff over time. As we age, our tissue ages too. The tissue in our rotator cuff starts to thin and break-down. Any repetitive or frequent movement can place stress on your rotator cuff over the years. Your shoulder can also suffer degenerative changes such as arthritis, osteoarthritis and/or cartilage thinning on the ends of the bones. This gradual wear and tear in your shoulder comes for overuse, repetitive shoulder movements, arm lifting / lowering / rotation with weight bearing activities.
Degenerative changes to the shoulder happen slowly, so you may end up suffering with a rotator cuff tear from a simple daily activity. You need to be aware that this injury can happen to anyone and is not just isolated to athletes!
Repetitive overhead movements without properly warming up (lifting object overhead for work, chopping wood, swinging a hammer, participating in sports such as volleyball, baseball, tennis and rowing) can cause the supraspinatus tendon to weaken over time making it more prone to a tear, tear, and rupture.
Because supraspinatus tendon injuries are often a result of overuse, people over 40 are at greater risk of degeneration and rotator cuff tears due to the body's natural weakening of the soft tissue over time.
Slouching your neck and shoulders forward can also cause excess stress on your supraspinatus tendon because the space for your tendon between the bones in your shoulder become smaller. This can lead to rotator cuff tendons becoming pinched by the bones in your shoulder.
Lack of strength to support the glenohumeral joint of your rotator cuff leads to a greater risk of incorrect movements. This can cause wear and tear on a tendon and weakening over time.

The best way to diagnose this condition is with a quick visit to the your doctor for a physical examination of your shoulder. Range of motion tests will be done to see how much movement has been lost in the shoulder.
Your doctor may also consider any previous shoulder injuries or joint stiffness that you may have had in the past. This will help the doctor to determine if you have a more complex injury in your shoulder and rule out any other rotator cuff injuries that may be present.
A set of range of motion and strength tests will be completed by the doctor including the Drop Arm Test. Your doctor will measure the number of degrees your arm can move when rotating. In the drop arm test, your doctor will ask you to put your arm out to the side and up towards your head. They will then ask you to move your arm back slowly to see if your arm will drop quickly on its' own because of a tear.
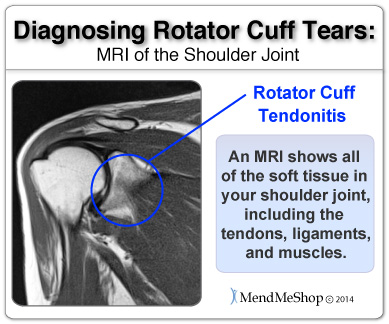
Your doctor may suggest diagnostic testing to obtain more detailed information, and assess the amount and/or type of damage done to your supraspinatus tendon. There are a variety of different tests available to help them analyze the situation; and the recommendation will be dependent on your injury. X-rays will provide an image of the overall bone structure of your shoulder. It's helpful in identifying abnormal bone shapes, fractures, arthritis, osteoarthritis, bone spurs or loose bones and bone abnormalities that may mimic a tear.
Other tests like a bone scan, MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) or blood tests may be done if an x-ray looks normal or the doctor is unsure whether you have a fracture. These tests will also rule out any infections of the bone or tissue and help to determine if you are suffering from other injuries like arthritis or osteoarthritis (degenerative damage).

Supraspinatus tears are known to be difficult to heal as the rotator cuff area in the shoulder is a very complicated arrangement of tissue in multiple layers. The rotator cuff is made up of muscles, tendons, and ligaments that form a 'cuff' attached to the upper arm bone (humerus), 'wing' bone (scapula), and collar bone (clavicle) in your shoulder. It is possible to get a tear in your rotator cuff that is actually a tear in a tendon (attachment point between muscle and bone), muscle, or ligament (tissue attaching bone to bone. Your tear could be located in the teres minor, infraspinatus, supraspinatus, subscapularis area of the tendons. It's also possible to get a tear in the coracoclavicular, acromioclavicular, coraco-acromial, coraco-humeral, transverse humeral, superior glenohumeral, middle glenohumeral or inferior-glenohumeral area of your ligaments.
Rotator cuff tears in a tendon or ligament receive very little natural blood supply. It's the lack of blood flow around your tear that makes rotator cuff injuries so hard to heal. Healing will be a battle no matter what course of treatment your doctor's suggesting but they will try to focus on minimizing further damage and giving the body rest and adequate blood flow to accelerate the healing of your supraspinatus. In our opinion, the localized enhanced circulation from a TShellz Wrap® take home conservative treatments one step further by stimulating your bodys recovery process while minimizing re-injury and over-compensation risk.
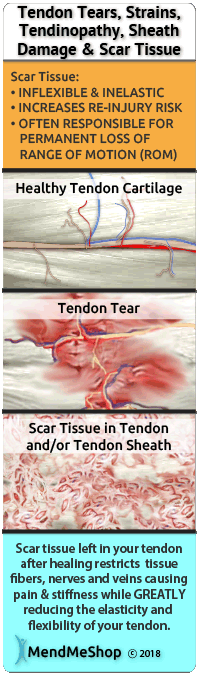
Constant re-injury (you know when it's happening, you can feel the pain) needs to be avoided at all costs. Obviously, it delays the healing process, but what's worse is that every re-injury and additional healing cycle increases the amount of scar tissue that builds up in and around your supraspinatus tear.
Scar tissue is hard, inflexible, and tough to get rid of. The more severe your supraspinatus injury is, the more likely that this scar tissue will fill into the tears in your supraspinatus, also attaching to all of the surrounding healthy tissue. This added scar tissue will restrict your ability to control the movement of your shoulder. Scar tissue also makes your supraspinatus much more prone to injury again later on. The more scar tissue that develops, the more you lose the range of motion in your entire shoulder joint.
Continuous re-injury and build-up of scar tissue while staying active means you'll have a greater chance of winding up with on-going pain, more tearing in your rotator cuff and tearing or weakening (atrophy) of surrounding tissue (ligaments, tendons, muscle).
If you have pain and inflammation in your shoulder, it's very important to heal your injury quickly and completely. You must avoid the build up of scar tissue. If you don't, your supraspinatus injury may plague you forever. This is why it's so important to continuously use conservative treatment tools to heal any recurring supraspinatus damage before it can build into something big. For any rotator cuff tear sufferer, having the right tools means all the difference.
Everything in the human body is connected. Any supraspinatus injury can lead to other injuries over time if not treated properly. You might start lifting with and using your opposite arm when performing normal daily activities, like brushing your teeth, brushing your hair, carrying or reaching for things. You may also try to rely on your opposite (healthy / stronger) shoulder and arm to get yourself back to work, activities or your sports sooner to avoid waiting for your supraspinatus injury to heal completely.
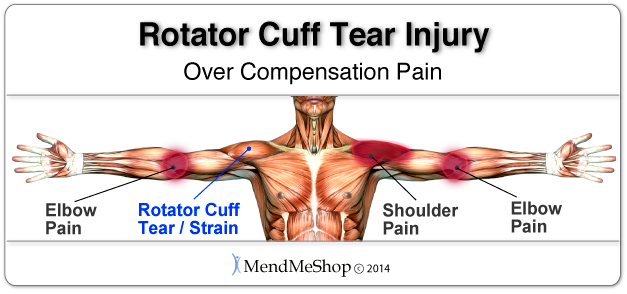
Many of our clients have experienced pain in the affected arm's elbow and their opposite elbow or shoulder because they shift their lifting weight and use to the opposite arm. For example, you might normally reach for items off of higher shelves with your right arm, but instead will use your left arm while your right arm heals. Even though changing something like this seems like a really small thing, changing the way you would normally reach and grab for things when your body isn't used to that can result in pain and injuries in your healthy arm.
Over time you'll notice that you automatically start to put more weight on your non-injured side to cope with everyday activities. When you experience pain on the opposite side of your body, this is something called "over compensation" pain. Usually the supraspinatus will get torn in your dominant shoulder (if you are right handed, this would be your right shoulder). When this happens there is a higher risk that you'll over-strain your weaker arm that's compensating for your injury, because it's just not as strong as your dominant side.
Even if you try to avoid over compensation pain in your healthy arm you're still at risk for re-injuring your damaged supraspinatus. Ignoring over compensation pain and the pain felt from your supraspinatus injury while returning to regular activities or your job can lead to even more problems with healing.
Many of these objectives go hand in hand (ie. the faster you heal, the less risk you have of re-injury) and know that the Shoulder TShellz Wrap® is highly effective in reaching all of these objectives. It is basically the best home-based soft tissue recovery tool you will find! The 1st Stage is reducing pain and swelling to open up your blood flow. This can be done by using any off the shelf cold wrap or ice pack.
Once the swelling is gone and your blood vessels are opened up, you can really start to get your recovery fast tracked by treating yourself every day with the Shoulder TShellz Wrap®.
If you have a torn rotator cuff, it's very important to heal it quickly and completely. Minimizing the healing time should be an obvious goal, as a chronic rotator cuff tear will limit your ability to go about your daily routine for a long period of time.
A seemingly small, nagging injury in your shoulder that's not properly treated can lead to a chronic painful degenerative rotator cuff injury that can persist for months or even years if not properly treated.
Product Advisors are available 9:00 am to 5:00 pm Eastern Standard Time Monday to Friday.
I want to learn more about Post-Surgery Recovery
I want to learn more about TShellz Wrap® Circulatory Boost
I want to learn more about Ice & Heat: Which Is Better For Treatment?
I want to learn more about Tendonitis Treatments
I want to learn more about Tendonitis Surgery
During your recovery, you will probably have to modify and/or eliminate any activities that cause pain or discomfort at the location of your soft tissue injury until the pain and inflammation settle. The more diligent you are with your treatment and rehabilitation, the faster you will see successful results!
Please be aware that this information is neither intended nor implied to be a substitute for professional medical advice. CALL YOUR HEALTHCARE PROVIDER IMMEDIATELY IF YOU THINK YOU MAY HAVE A MEDICAL EMERGENCY. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider before using any of our outstanding products to make sure they are right for you and your condition or if you have any questions regarding a medical condition. Always see your doctor for a proper diagnosis as there are often many injuries and conditions (some very serious) that could be the cause of your pain.
© 2025 In.Genu Design Group, Inc. Contact Us